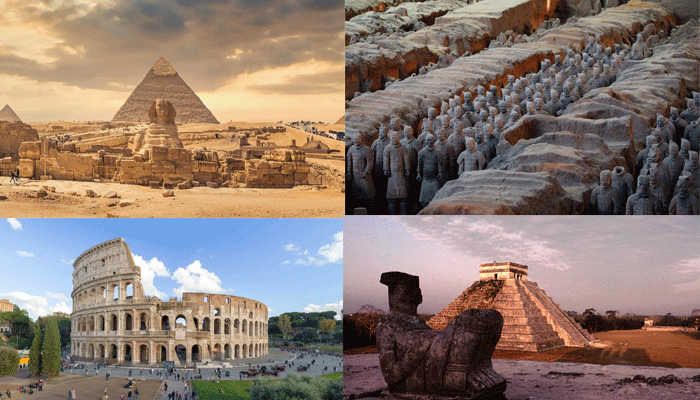

Civilization is a term that describes a form of human society that exhibits some distinctive features, such as urbanization, social stratification, political organization, writing, art, religion, and science. The origin and development of civilization is a fascinating and complex topic that has intrigued historians, archaeologists, and anthropologists for centuries. In this blog post, we will explore the history of six early civilizations that emerged in different regions of the world, and learn about their period, achievements, challenges, and contributions to humanity.
Indus Valley
The Mysterious Civilization (2500 BCE – 1900 BCE)
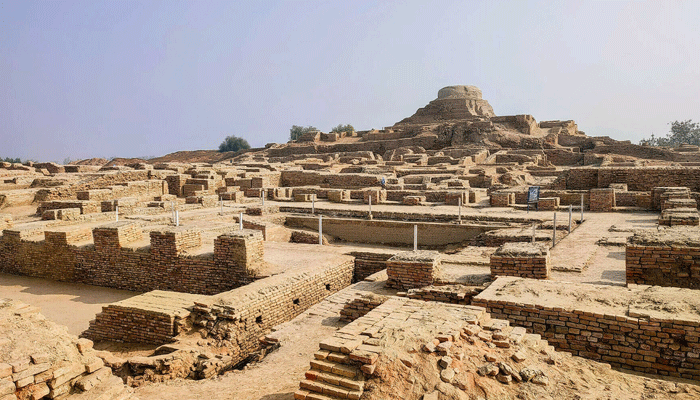

The Indus Valley civilization, also known as the Harappan civilization, was one of the earliest and largest civilizations in the world. It flourished in the Indus River basin in what is now Pakistan and northwest India from about 2500 BCE to 1900 BCE. The Indus Valley civilization is known for its urban planning, sanitation, trade, and writing system. The Indus Valley civilization built impressive cities, such as Harappa and Mohenjo-Daro, which had grid-like streets, brick houses, drainage systems, public baths, and granaries. The Indus Valley civilization also had a sophisticated trade network that connected it with other civilizations, such as Mesopotamia and Egypt. The Indus Valley civilization developed a unique writing system, which had not been deciphered yet, and used seals, weights, and measures for commerce and administration. The Indus Valley civilization is mysterious because we do not know much about its culture, religion, politics, or decline. Some possible causes of its collapse include environmental changes, invasions, or internal conflicts.
Mesoamerica
Exploring the 6 Early Human Civilizations in the World(1200 BCE – 1521 CE)
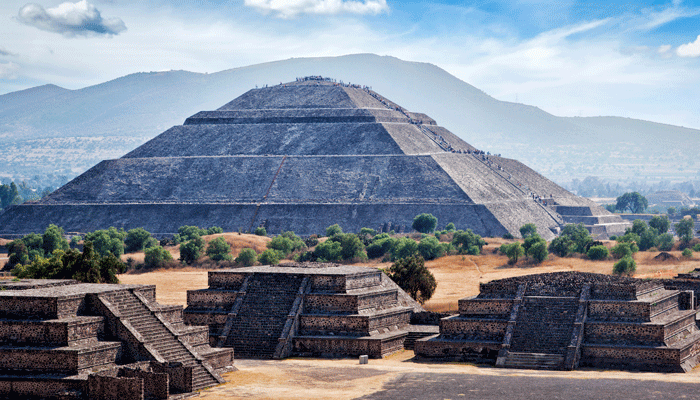

Mesoamerica, located in Central America, was the cradle of ancient civilizations such as the Olmec, Maya, Teotihuacan, Toltec, and Aztec. This region stands out for its cultural diversity, artistic expression, and scientific advancements. Mesoamerican civilizations pioneered intricate calendars, mathematics, astronomy, and writing systems. Monumental structures like pyramids, temples, palaces, and ball courts showcased their architectural prowess. Embracing diverse polytheistic religions, Mesoamerican civilizations engaged in rituals, sacrifices, and ceremonies. Dynamic and sometimes violent interactions unfolded both among these civilizations and with the European invaders of the 16th century. Iconic figures and events, including the Maya Long Count calendar predicting the 2012 apocalypse, the demise of Aztec emperor Montezuma II at the hands of Spanish conquistador Hernan Cortes, and the Popol Vuh, the sacred book of the Maya, contribute to the captivating narrative of Mesoamerican history. Embark on an exclusive exploration of this rich history with the Secret Escapes UK Discounts.
Ancient Greece
The Birthplace of Western Civilization (800 BCE – 146 BCE)
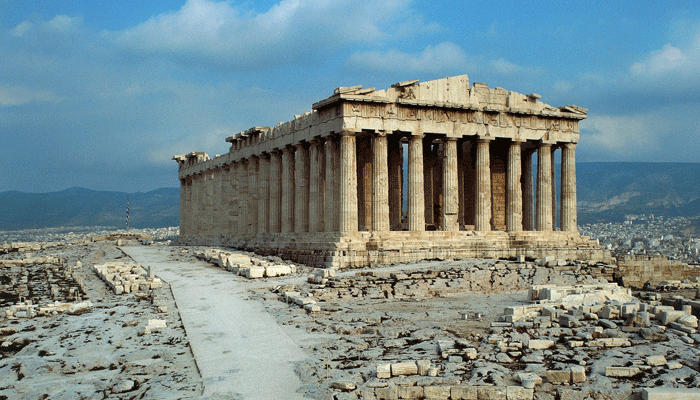
Ancient Greece is a civilization that flourished in the eastern Mediterranean, especially on the mainland and the islands of the Aegean Sea. Ancient Greece is considered the birthplace of Western civilization, as it was the origin of democracy, philosophy, literature, drama, art, science, and sports. Ancient Greece was composed of many independent city-states, such as Athens, Sparta, Corinth, and Thebes, which competed and cooperated. Ancient Greece also fought against foreign invaders, such as the Persians and the Macedonians, and spread its culture and influence throughout the Mediterranean and beyond. Some of the most famous figures and works of ancient Greece include Homer (the author of the epic poems The Iliad and the Odyssey), Socrates (the founder of Western philosophy), Plato (the student of Socrates and the author of the Republic), Aristotle (the teacher of Alexander the Great and the father of logic and science), the Parthenon (a temple dedicated to the goddess Athena), the Olympic Games (a festival of athletic competitions), and the Trojan War (a legendary war between the Greeks and the Trojans).
Ancient Rome
The Eternal City (753 BCE – 476 CE)
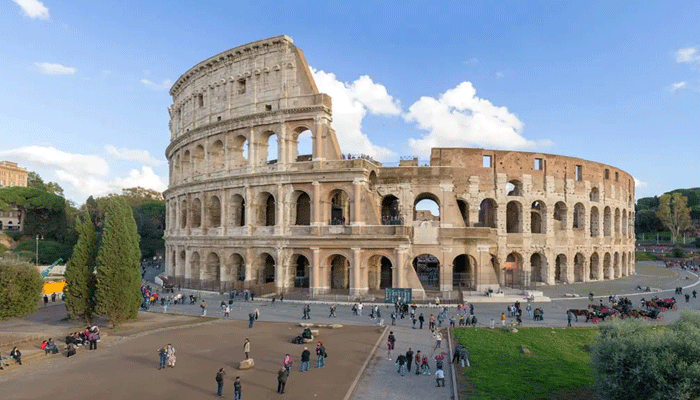

Ancient Rome is a civilization that rose from a small city on the banks of the Tiber River in central Italy to become the dominant power in the Mediterranean and Europe. Ancient Rome was first a republic, governed by elected officials and a senate, and then an empire, ruled by emperors who wield absolute authority. Ancient Rome was known for its military prowess, legal system, engineering feats, and cultural achievements. Ancient Rome also assimilated and integrated many aspects of the civilizations it conquered, such as Greece, Egypt, and Persia. Some of the most famous monuments and events of ancient Rome include the Colosseum (an amphitheater for gladiator fights and other spectacles), the Pantheon (a temple for all the gods), the aqueducts (structures that carried water from distant sources), the roads (networks that connected the vast empire), the Pax Romana (a period of peace and prosperity), and the fall of Rome (a complex process of decline and collapse).
Ancient China
The Middle Kingdom (2000 BCE – 1912 CE)
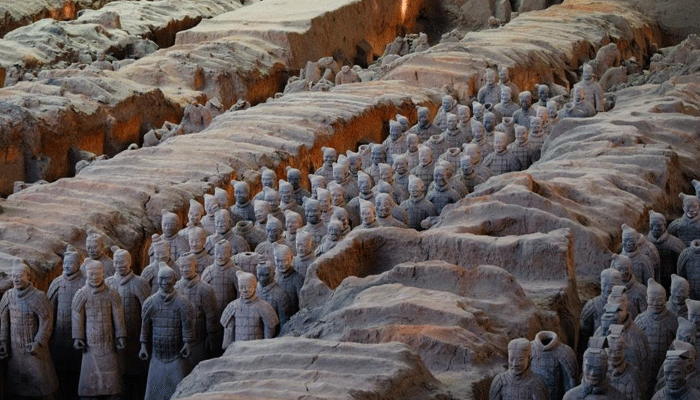

Ancient China is one of the oldest and longest-lasting civilizations in the world, with a continuous history of over 4000 years. Ancient China is also one of the most influential and diverse civilizations, with a rich and varied culture, language, philosophy, and religion. Ancient China was ruled by various dynasties, such as the Shang, the Zhou, the Qin, the Han, the Tang, the Song, the Yuan, the Ming, and the Qing, each of which left their mark on the history and culture of China. Ancient China was also the source of many inventions and discoveries, such as paper, printing, gunpowder, compass, porcelain, silk, tea, and the Great Wall.
Ancient Egypt
The Land of the Pharaohs (3100 BC – 332 BCE)
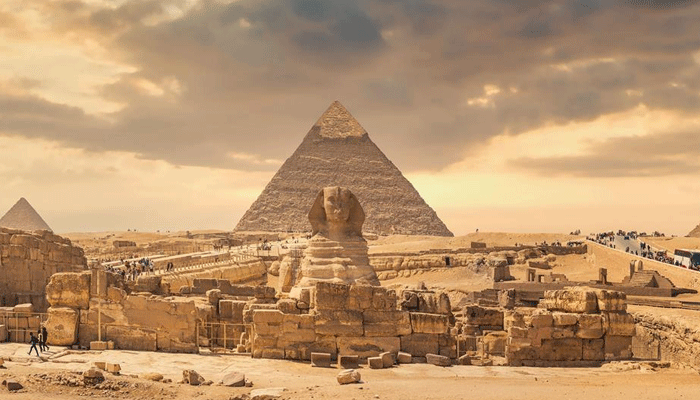

Ancient Egypt, nestled along the Nile River in northeastern Africa, stands as a testament to the grandeur of ancient civilizations. Renowned for its imposing pyramids, constructed as eternal resting places for divine pharaohs, Egypt left an indelible mark on history. The hieroglyphs, an intricate writing system utilizing symbols and images, were a distinctive feature of this advanced civilization. Ancient Egypt excelled in various fields, including art, architecture, engineering, agriculture, religion, and the art of mummification. Iconic landmarks such as the Great Sphinx, a colossal lion-headed statue, and historical artifacts like the Rosetta Stone, a crucial key in deciphering hieroglyphs, contributes to the cultural richness. The biblical tale of the Exodus, recounting the Israelites’ liberation from Egyptian slavery, adds a layer of historical significance. Embark on an immersive journey through ancient Egypt with the Travel Discount Code.
Conclusion
These are just some of the many civilizations that have shaped the history of the world. Each civilization has its own unique story, achievements, challenges, and contributions to humanity. By exploring the history of different civilizations with their period, we can learn more about ourselves, our past, our present, and our future. We can also appreciate the diversity and richness of human culture and the commonalities and connections that bind us together.








